No Products in the Cart
The Caffeine Crash: Why Does Coffee Make Me Sleepy?
It is generally believed that coffee can wake you up and feel refreshed, but have you ever had a cup f coffee while experiencing greater sleepiness? And even along with difficulty concentrating, being sensitive and irritable, dozing, and other phenomena, which may be a "caffeine crash". Many people may have experienced a "caffeine crash", let's dive into this article and see what is going on.
Mechanism of action of coffee

The main component of caffeine is 1,3,7 - trimethylxanthine, which is similar in structure to adenosine in the human body. Adenosine is a component of nucleic acid and ATP, which is the product of energy released from human cells. The more adenosine a person has in a waking situation, the more nerves check the rising level of adenosine in the body, and the more sleepy a person is likely to be. Caffeine blocks the function of adenosine by occupying adenosine receptors to achieve the effect of refreshing.
1.Metabolic overload
Caffeine consumption over an extended period of time will accelerate metabolic rate, consuming vitamin B complex in your body, and nerve and muscular coordination. One sign of vitamin B insufficiency is easily feeling fatigued. Long-term coffee intake causes the body to become less sensitive to the stimulant effects of coffee, thus the same amount does not appear to play a beneficial role. Anemia, loss of appetite, dermatitis, epilepsy, schizophrenia, memory loss, and drowsiness can be the symptoms of vitamin B complex deficiency.

2.Increased body temperature
The intake of hot coffee also leads to a rise in body temperature, which allows lethargy to take over your brain before the coffee acts on your nerves. Blood vessels in the body will enlarge when body temperature increases to aid in heat dissipation. Although the blood flow in the cerebral blood vessels has risen, the pressure in the brain, which contributes to vertigo and readily induces sleep, will change as a result of the increase in blood flow.
3.Dehydrated by caffeine
For most people who get sleepy from drinking coffee, what can bother them is the problem of dehydration.
In addition to being stimulating, for most of us, caffeine acts as a diuretic, increasing the frequency of trips to the bathroom and risking dehydration. Blood thickens and travels more slowly through your body's circulatory system, which supplies less oxygen to the brain and other organs and makes your brain more sluggish and hazy. The body loses water which is essential to its correct operation. The fact that coffee also has a vasoconstrictive impact, which can momentarily constrict your veins and arteries, makes the issue more complicated. As a result, the whole process can happen very quickly, and shortly after the problem becomes more serious, you will be dehydrated and have the illusion that coffee is making you drowsy.
For your information, most of us are usually already in a state of under-hydration.
For optimal health and proper body function, the World Health Organization usually recommends that you drink at least 2 liters of water.

4.Sweet tooth
While homemade vanilla coffee or a variety of iced strawberry iced coffees can really make a wonderful effect on you, the sweeteners added to coffee may have a negative effect on you.
Drinking sugary coffee drinks may lead to sleepiness as the body absorbs too much sugar to create a feeling of lethargy. Sugar is metabolized in the body much faster than caffeine and can lead to fatigue at the end of the breakdown process. Therefore, with certain coffee choices, the depleting effect of the sugar crash may hit you faster than the energy boost from caffeine, leading to fatigue and even making you drowsy.
A recent study shows the fact that caffeine can raise blood sugar levels. Research in 2016 found a link between excessive caffeine intake and reduced insulin sensitivity, increased insulin resistance, and elevated blood glucose levels. Even brief elevations in blood sugar (if high enough) can lead to fatigue, headaches, poor concentration, frequent urination, and dehydration (all symptoms that put you to sleep).
5.Adenosine blockade
Coffee keeps us awake because caffeine blocks the adenosine receptors in the brain and prevents them from detecting critical chemical signals. If it takes several hours for the coffee-induced sleepiness to hit you, you may have run out of caffeine and your nerves are gradually approaching the adenosine wall.
Adenosine is an endogenous neurotransmitter that causes fatigue, and once caffeine blocks its pathway, you are temporarily protected from fatigue, resulting in higher energy levels. However, during the blockade, the processes responsible for adenosine activity do not stop. They gradually increase in an attempt to counteract the perceived adenosine resistance. Therefore, when the effects of caffeine wear off, the adenosine buildup load immediately hits you, resulting in a caffeine "high followed by a loss of energy" and causing sleepiness.

6.Caffeine-resistance
Another possible reason you may experience a lethargic crash just a few hours after consuming espresso is that you may have developed a tolerance to caffeine.
Many people who regularly consume caffeinated beverages complain of developing a tolerance to their stimulating effects. One possible explanation for this is that the frequent adenosine overdose hypersensitivity causes the muscle to develop new physiological standards. Thus, more coffee intake is required to obtain the same effect in smaller doses.
However, a study by the Military Nutrition Research Council of the Institute of Medicine showed that no evidence was found for the body breaking down or absorbing caffeine, even with continued exposure.
7.Other factors
A cup of coffee won't overshadow other lifestyle choices for long, and if you are chronically sleep deprived, dehydrated, or under high stress, you may find yourself dizzy even if you take a lot of caffeine.
Tips: Other lifestyle choices that can seriously affect your energy levels include a sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, inadequate nutrition, poor exercise habits, and sleep disorders such as sleep apnea.

Who is not a good candidate for coffee?
1.Patients with intestinal diseases
The caffeine contained in coffee can irritate the stomach mucosa and aggravate the gastrointestinal diseases. Coffee promotes gastric acid secretion, which may lead to lower esophageal sphincter relaxation and aggravate acid reflux symptoms, belching, and other gastrointestinal discomfort symptoms to worsen.

2.Slow metabolizers
Coffee will increase the excitement of the nervous system, if the metabolism of caffeine is slow, there may be palpitations, insomnia, etc.
3.People with mental illness
Caffeine has an effect on the nervous system and for patients suffering from mental illnesses such as anxiety disorders, coffee intake can enhance anxiety
How to drink coffee without feeling tired?
It is better to drink black coffee
Avoid post-sugar weakness by sticking to black coffee whenever possible. A little sweetener can help neutralize the bitterness of your coffee, but avoid taking in too much sugar or syrup, or cream again to ensure optimal energy levels after drinking.

Have a good night’s sleep
Taking enough sleep is the best way to avoid sleepiness during the day. And we know there are so many factors that can affect your sleep, your daily exercises, the ambient noise, the alcohol intake, and a good mattress.
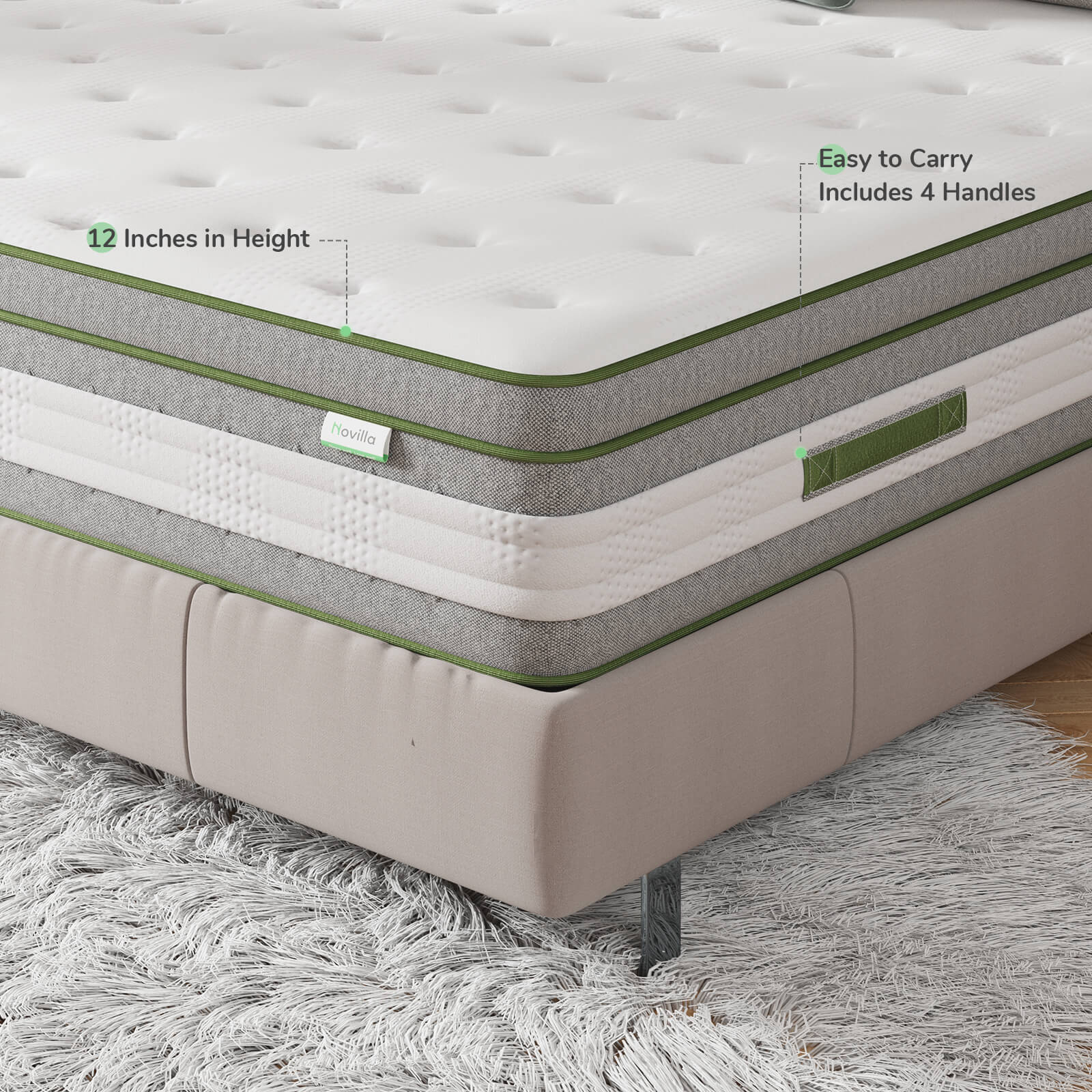
Novilla Serenity Hybrid Mattress can promote enough airflow to ensure the mattress sleep cool even though with multiple layers of memory foam on top. Gel-infused memory foam can capture and release body heat. Another great feature of this mattress is that it has superb motion isolation due to the individually pocketed coil arrangement, allowing you can have targeted pressure relief and sleep support. The bamboo rayon fiber cover is hypoallergenic and breathable so that you can enjoy a peaceful and restful night’s sleep.

FAQs
1.Drinking coffee makes people dumber?
It is a ridiculous rumor, the right amount of coffee refreshes the brain Caffeine stimulates the nervous centralis, making the mind more clear, quicker thinking, focusing, and improving work efficiency.
Additionally, caffeine helps to improve alertness, sensitivity, memory, and concentration. But drinking more coffee than you are accustomed to, will produce similar to consuming the same dose of stimulants, which can cause hypersensitivity. For people who tend to have anxiety disorders, caffeine can cause sweaty palms, heart palpitations, and tinnitus, which can worsen symptoms.
2.Can moderate amounts of caffeine reduce the risk of disease?
Caffeine has preventive (and palliative) properties for a number of neurodegenerative diseases, particularly Parkinson's and Alzheimer's. Caffeine works by blocking adenosine A2 to reduce the risk of disease and improve cognitive impairment.
3.What are some ways you can be more awake in the morning?
Caffeine can disrupt the sleep cycle, so don't consume caffeine 6 hours before bed, so that your body can enter the “time-to-sleep” status and get quality sleep. Getting a good night's sleep helps to be more clear and refreshed in the morning, avoid sleeping too late at night to make sure you have 7 to 9 hours of restful sleep each night.
Conclusion
Our deepening awareness of coffee is gradually changing the way we view it. Therefore, I would like to offer some suggestions on how to stay awake without coffee. For example, spray cold water on your face and wrists, or drink a glass of warm water. And most importantly, have a healthy lifestyle! Excessive caffeine intake can prolong the length of light sleep and shorten the length of deep sleep, which can create a vicious cycle. Getting enough sleep is the right way to improve efficiency!
Related Posts:

Freshen Up Your Sleep: Clean Mattress Tips

Can You Wash Pillows in Washer? Our Easy Guide.